With cryptocurrency, you can stake your digital assets to earn passive income. Staking refers to keeping cryptocurrency locked up to earn incentives or interest. It is similar to depositing cash in a high-yield savings account. You put your digital assets into a staking pool, earning interest on your account balance. According to TradingPlatforms.com, the annual return on staked crypto assets averaged 8.8% in the last 1 year.
Edith Reads, an analyst at TradingPlatforms.com, commented on the data. She said. ” Investors are exploring new ways to make money from their digital assets. Staking is becoming increasingly popular as it offers a way to earn passive income without selling your cryptocurrencies.”
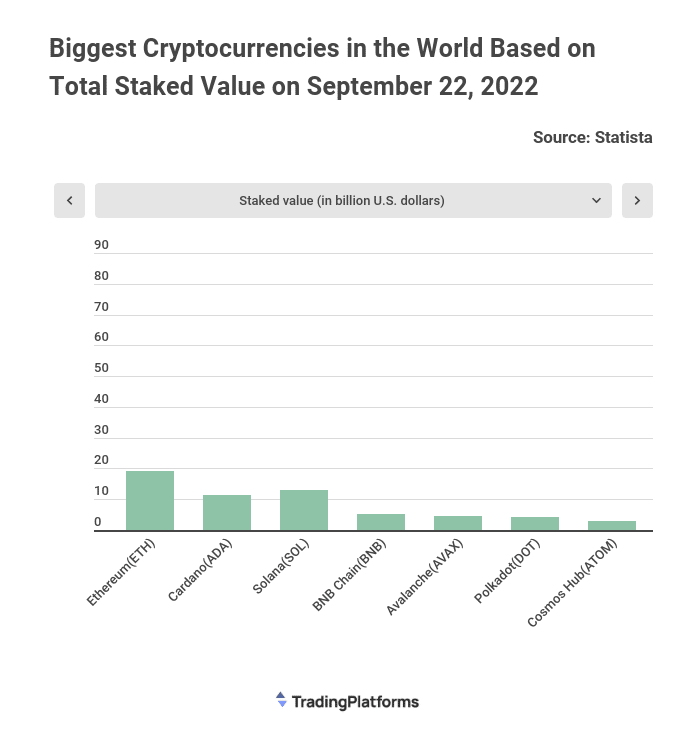
Reads continued, “The recent Ethereum upgrade highlights staking opportunities for institutional holders. In the short term, however, liquidity is still an issue. Institutional staking of crypto assets could be a ‘phenomenon’ in the future as soon as the market overcomes its liquidity lock-up.”
What is Cryptocurrency Staking?
Cryptocurrency staking is the process of holding funds in a cryptocurrency wallet to support the operations of a blockchain network. Most often, the process involves participating in consensus by locking up funds as collateral to validate transactions and produce new blocks, thus earning staking rewards.
How Cryptocurrency Staking Works
Staking works by locking up funds as collateral to validate transactions and produce new blocks. In return for staking, participants earn rewards proportional to the amount of funds they have staked. The size of the reward also depends on the specific cryptocurrency being staked and the rules of the network.
Investors’ holdings are used to “write” information into a new block and verify its authenticity. Because blockchain information is “baked” into coins, it can verify transactions. Afterward, the staker receives a payout from the network for allowing their assets to confirm.
Proof of Stake (POS) Consensus Mechanism
The consensus mechanisms used by most cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin (BTC), are called Proof of Work (PoW). PoW is a system that uses computational power to solve complex mathematical problems in order to validate transactions and produce new blocks. The first person to solve the problem gets to write the new block into the blockchain and receives a reward for their work.
In contrast, PoS consensus mechanisms do not rely on computational power to validate transactions and produce new blocks. Instead, they use cryptocurrency holders’ stakes as collateral. The more currency you stake, the greater your chances of being chosen to validate a transaction and produce a new block. And like with PoW, the block validator receives a reward for their work.
The key difference between PoW and PoS is that, with PoS, you can earn rewards even if you’re not the one chosen to validate transactions and produce new blocks. As long as you have staked currency, you will earn a share of the rewards given to block validators. This makes staking a more energy-efficient way of maintaining a blockchain network.
What Are the Risks of Staking Cryptocurrency?
As with any investment, there are risks associated with staking cryptocurrency. The value of your stake can go up or down, and you could lose money.
There is also the risk that the cryptocurrency you are staking could become worthless if the project fails. This is a particular risk with smaller, less well-known cryptocurrencies. Before staking any cryptocurrency, be sure to do your own research and only invest what you can afford to lose.

Question & Answers (0)